CSDNCurrent en:Example Project
Setting up the development environment
We highly recommend you to use an IDE for the following tutorial. The code has successfully been tested with Visual Studio Community.
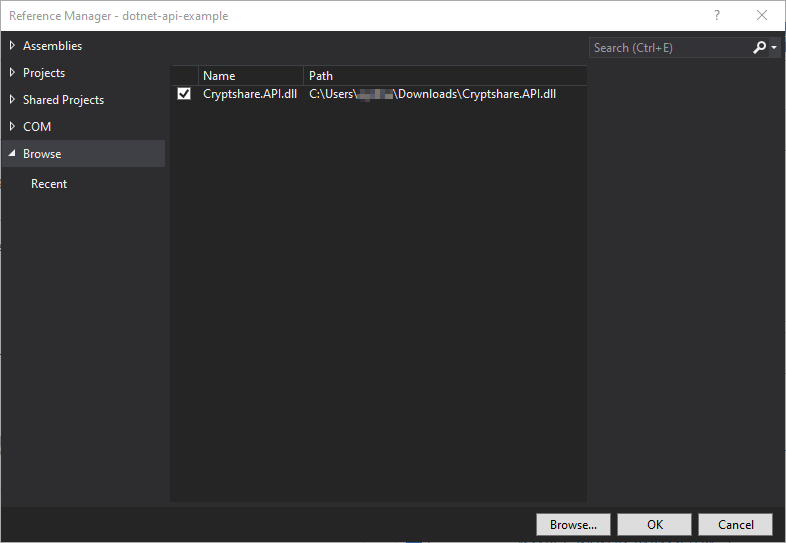
After launching the IDE and creating your Visual Studio Solution and Project, please add the Cryptshare.API.dll to the project references:
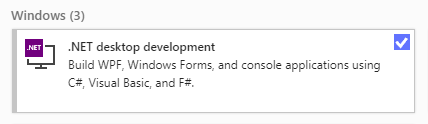
Also make sure that you have installed the ".NET desktop development" tools using the Visual Studio Installer:
Performing your first transfer
Below is a sample program that performs a Cryptshare transfer from a specific sender to a specific recipient. You may adjust the individual properties to your needs and, if all prerequisites have been considered, perform the transfer.
using Cryptshare.API;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace CryptshareTransfer
{
class Program
{
private static readonly string SenderEmailAddress = "alice@example.com";
private static readonly string SenderName = "Alice";
private static readonly string SenderPhoneNumber = "+1 (123) 4567 890";
private static readonly string ServerUrl = "https://cryptshare.example.com";
// New "client.store" file will be created if it doesn't already exist.
// However, make sure the folder exists and is writable by the user running this program!
private static readonly string ClientStoreLocation = @"C:\temp";
private static readonly string RecipientEmailAddress = "bob@example.com";
private static readonly List<string> FilePaths = new List<string>() { @"C:\temp\pdf-sample.pdf" };
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
// Initialize the Client object.
Client client = new Client(
SenderEmailAddress,
new CryptshareConnection(new WebServiceUri(ServerUrl)),
ClientStoreLocation
);
// Initialize the Transfer object.
Transfer transfer = new Transfer();
// Define the sender and recipient information.
transfer.SenderName = SenderName;
transfer.SenderPhone = SenderPhoneNumber;
transfer.Recipients.Add(new Recipient(RecipientEmailAddress));
// Define the list of files to be sent.
transfer.Files = FilePaths;
// Optional: Let the Cryptshare Server handle the email sending process.
transfer.SendEmails = true;
transfer.NotifySender = true;
transfer.NotifyRecipients = true;
transfer.InformAboutDownload = true;
// Ensure that the client is verified.
CheckVerificationResult checkVerificationResult = client.CheckVerification();
if (!checkVerificationResult.Verified)
{
if (checkVerificationResult.VerificationMode == VerificationMode.Client)
{
Console.WriteLine("Please authorize the following Client ID on the Cryptshare Server:");
Console.WriteLine(client.ClientId);
return;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"Requesting a verification code for {client.UserEmailAddress}...");
client.RequestSenderVerification();
Console.WriteLine($"Please enter the code below and confirm with [Enter]:");
string code = Console.ReadLine().Trim();
client.ConfirmSenderVerification(code);
}
}
// Request a generated password of a minimum length specified by the server.
transfer.PasswordMode = PasswordMode.Generated;
int minimumPasswordLength = client.RequestPasswordPolicy().MinimumLength;
transfer.Password = client.RequestGeneratedPassword(minimumPasswordLength);
// Set the transfer expiration date to the maximum storage duration.
Policy policy = client.RequestPolicy(transfer.Recipients.ConvertAll(recipient => recipient.EmailAddress));
transfer.ExpirationDate = DateTime.Now.AddDays(policy.StorageDuration);
client.PerformTransfer(transfer,
HandleUploadProgressChanged,
HandleUploadComplete,
HandleUploadInterrupted,
HandleUploadCancelled);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.Error.WriteLine("An error has occurred: " + e);
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to terminate the program.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
private static void HandleUploadProgressChanged(string currentFileNo,
string currentFileName,
double bytesUploaded,
double bytesTotal,
long bytesPerSecond)
{
// Print a status line every time the upload progress has changed.
int percent = (int)(bytesUploaded / bytesTotal * 100);
string speedInMbs = $"{((double)bytesPerSecond / 1024 / 1024).ToString("0.00")} MB/s";
string statusLine = $"Filename: {currentFileName}\tProgress: {percent}%\tSpeed: {speedInMbs}";
Console.Write($"\r{statusLine}");
}
private static void HandleUploadComplete(IDictionary<string, string> urlMappings,
IDictionary<string, string> smtpMappings,
string serverGenPassword,
TransferError transferError,
string trackingID)
{
// Reveal the final transfer information to the sender.
Console.WriteLine("\nUpload finished!");
Console.WriteLine("URL mappings:");
foreach (var mapping in urlMappings)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{mapping.Key} => {mapping.Value}");
}
Console.WriteLine("SMTP mappings:");
foreach (var mapping in smtpMappings)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{mapping.Key} => {mapping.Value}");
}
Console.WriteLine($"Tracking ID: {trackingID}");
}
private static void HandleUploadInterrupted(CryptshareException exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("The upload has been interrupted by the server!");
}
private static void HandleUploadCancelled()
{
Console.WriteLine("The upload has been cancelled by the user!");
}
}
}
While the example above demonstrates the main use case for Cryptshare—securely sending files and messages—combining the Cryptshare Server with the .NET API allows you to cover a broad range of applications. As as example, we will demonstrate a program that builds on top of the example above, but extends it with the functionality of watching a folder and performing a synchronous transfer for each new file that is offloaded to a specific directory. The example is deliberately kept simple in order to focus on the API functionality itself.
using Cryptshare.API;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
namespace CryptshareFolderWatcher
{
class Program
{
private static readonly string SenderEmailAddress = "alice@example.com";
private static readonly string SenderName = "Alice";
private static readonly string SenderPhoneNumber = "+1 (123) 4567 890";
private static readonly string ServerUrl = "https://cryptshare.example.com";
// New "client.store" file will be created if it doesn't already exist.
// However, make sure the folder exists and is writable by the user running this program!
private static readonly string ClientStoreLocation = @"C:\temp";
private static readonly string RecipientEmailAddress = "bob@example.com";
private static string WatchPath;
private static string DonePath;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
if (args.Length != 2)
throw new ArgumentException("Exactly two path parameters need to be provided.");
WatchPath = args[0];
DonePath = args[1];
using (FileSystemWatcher watcher = new FileSystemWatcher())
{
watcher.Path = WatchPath;
watcher.NotifyFilter = NotifyFilters.FileName;
watcher.Created += OnCreated;
watcher.EnableRaisingEvents = true;
Console.WriteLine($"Watching directory {WatchPath}... press 'q' and [Enter] to quit watching.");
while (Console.Read() != 'q') ;
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.Error.WriteLine("An error has occurred: " + e);
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to terminate the program.");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
private static void OnCreated(object sender, FileSystemEventArgs e)
{
SendFile(e.FullPath);
File.Move(e.FullPath, Path.Combine(DonePath, e.Name));
}
private static void SendFile(string filePath)
{
// Initialize the Client object.
Client client = new Client(
SenderEmailAddress,
new CryptshareConnection(new WebServiceUri(ServerUrl)),
ClientStoreLocation
);
// Initialize the Transfer object.
Transfer transfer = new Transfer();
// Define the sender and recipient information.
transfer.SenderName = SenderName;
transfer.SenderPhone = SenderPhoneNumber;
transfer.Recipients.Add(new Recipient(RecipientEmailAddress));
// Request a generated password of a minimum length specified by the server.
transfer.PasswordMode = PasswordMode.Generated;
int minimumPasswordLength = client.RequestPasswordPolicy().MinimumLength;
transfer.Password = client.RequestGeneratedPassword(minimumPasswordLength);
// Define the list of files to be sent.
transfer.Files = new List<string>() { filePath };
// Optional: Let the Cryptshare Server handle the email sending process.
transfer.SendEmails = true;
transfer.NotifySender = true;
transfer.NotifyRecipients = true;
transfer.InformAboutDownload = true;
// Ensure that the client is verified.
CheckVerificationResult checkVerificationResult = client.CheckVerification();
if (!checkVerificationResult.Verified)
{
if (checkVerificationResult.VerificationMode == VerificationMode.Client)
{
Console.WriteLine("Please authorize the following Client ID on the Cryptshare Server:");
Console.WriteLine(client.ClientId);
return;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"Requesting a verification code for {client.UserEmailAddress}...");
client.RequestSenderVerification();
Console.WriteLine($"Please enter the code below and confirm with [Enter]:");
string code = Console.ReadLine().Trim();
client.ConfirmSenderVerification(code);
}
}
// Set the transfer expiration date to the maximum storage duration.
Policy policy = client.RequestPolicy(transfer.Recipients.ConvertAll(recipient => recipient.EmailAddress));
transfer.ExpirationDate = DateTime.Now.AddDays(policy.StorageDuration);
client.PerformTransfer(transfer,
HandleUploadProgressChanged,
HandleUploadComplete,
HandleUploadInterrupted,
HandleUploadCancelled);
}
private static void HandleUploadProgressChanged(string currentFileNo,
string currentFileName,
double bytesUploaded,
double bytesTotal,
long bytesPerSecond)
{
// Print a status line every time the upload progress has changed.
int percent = (int)(bytesUploaded / bytesTotal * 100);
string speedInMbs = $"{((double)bytesPerSecond / 1024 / 1024).ToString("0.00")} MB/s";
string statusLine = $"Filename: {currentFileName}\tProgress: {percent}%\tSpeed: {speedInMbs}";
Console.Write($"\r{statusLine}");
}
private static void HandleUploadComplete(IDictionary<string, string> urlMappings,
IDictionary<string, string> smtpMappings,
string serverGenPassword,
TransferError transferError,
string trackingID)
{
// Reveal the final transfer information to the sender.
Console.WriteLine("\nUpload finished!");
Console.WriteLine("URL mappings:");
foreach (var mapping in urlMappings)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{mapping.Key} => {mapping.Value}");
}
Console.WriteLine("SMTP mappings:");
foreach (var mapping in smtpMappings)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{mapping.Key} => {mapping.Value}");
}
Console.WriteLine($"Tracking ID: {trackingID}");
}
private static void HandleUploadInterrupted(CryptshareException exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("The upload has been interrupted by the server!");
}
private static void HandleUploadCancelled()
{
Console.WriteLine("The upload has been cancelled by the user!");
}
}
}
The resulting program should be usable as follows:
Datei:CryptshareFolderWatcher.mp4
Your browser does not support the HTML5 video element
Conclusion
As you can see, building solutions using the Cryptshare .NET API is very straightforward and allows you to perform tasks otherwise not possible with just the core product. We hope that this guide will help you with incorporating Cryptshare to your automation workflow.